The world is still coming to terms with the impact COVID-19 has had on our mental health. Since the start of the pandemic, there has been a significant increase in the demand for mental health professionals in Canada. As the focus and conversation around mental health continue to grow, so does the need for qualified experts who are adept at providing timely support and guidance to those in need.
With a career in therapy, one can not only respond to these rising demands but also make a real difference in the community.
This blog is a step-by-step guide to becoming a therapist in Canada. We will explore the role of a therapist, and the educational requirements and work experience considerations for becoming a registered therapist in your province.

Who is a Therapist?
The American Psychological Association (APA) defines a therapist as an individual who has been trained in and practices one or more types of therapy to treat mental or physical disorders or diseases. They help individuals, couples, and families address emotional, psychological, and behavioral issues to improve their overall well-being.
What is the difference between a therapist, psychologist, and psychiatrist?
Now that we understand who a therapist is, the differences are easier to list.
A psychiatrist has a medical degree and can diagnose clients with mental illnesses and prescribe medications.
A psychologist on the other hand has a degree in psychology and can diagnose mental health issues but cannot prescribe medication.
A therapist does not diagnose or prescribe medication for mental illnesses but primarily uses talk therapy to help with mental health issues.
How to Become a Therapist?
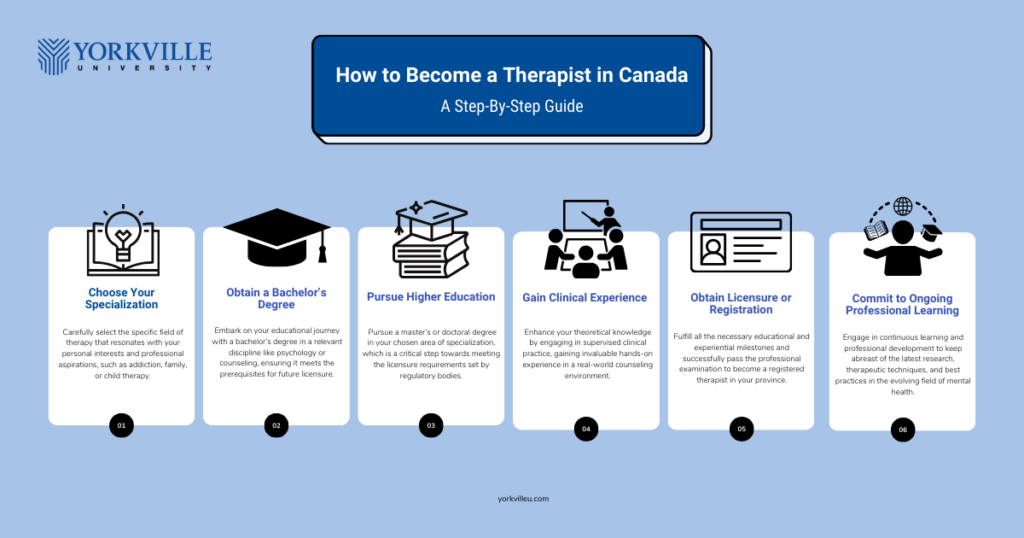
Broadly speaking, the path to becoming a therapist in Canada includes three steps: relevant education, experience, and licensure. Let us further elaborate on the process to include everything you need to know about how to become a therapist in Canada.
Step 1: Choose Your Specialization
The first step when researching the right program for you is to determine the area of therapy that aligns with your interests and career goals. Some of the areas of specialization include addiction, crisis and trauma, couple and family, and child therapy.
Step 2: Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree
Your education and experience all lead up to fulfilling the prerequisites for licensure or registration in your province. Your educational journey starts with a four-year equivalent bachelor’s degree in psychology, counselling, or other related disciplines. Ensure that the program you choose aligns with the educational requirements of the regulatory body in your province.
Step 3: Pursue Higher Education
Talking of educational requirements, many if not all regulatory bodies list completing a master’s degree or doctorate in your chosen therapy specialization as one of the licensure prerequisites. Some programs, like the Master’s in Counselling Psychology at Yorkville University, allow you to fulfill the educational requirements of more than one provincial regulatory body.
Step 4: Gain Clinical Experience
When it comes to a career as a therapist, skills practice makes perfect. You have acquired a lot of knowledge through your degrees, now is the time to put them to practice in a supervised clinical setting. Some universities offer a robust practicum as part of their programs, which is a great advantage over others that do not.
What if your program does not offer a practicum? You still have options. You can take up volunteering opportunities in mental health organizations, community centers, or crisis centers. These opportunities can provide valuable exposure to real-life counseling scenarios and the experience of working with a diverse population.
Step 5: Obtain Licensure or Registration
All that you do from steps 1 to 4 leads up to this. The path to becoming a registered mental health professional in your province includes completing relevant education, fulfilling clinical experience requirements, and, in some cases, passing the licensure examination. We have listed the regulatory bodies for some of the provinces in Canada below.
Step 6: Continue Professional Development
The field of mental health is ever-evolving, and it is important to maintain professional currency to ensure long-term career growth and efficiency of practice. You can do this by staying updated on research and practices through workshops, professional conferences, and additional certifications.
How to Become a Therapist in Your Province
It is essential to register with the regulatory body governing the profession in your province to practice as a therapist in Canada.
While the requirements of the regulatory bodies differ from province to province, here are the licensure requirements for becoming a therapist in these provinces.
How to Become a Therapist in Ontario
To become a practicing therapist in Ontario you will need to:
- Complete of a master’s degree in psychotherapy or a related field.
- Undergo supervised practice.
- Pass the College of Registered Psychotherapists of Ontario (CRPO) examination.
Here is one of only two online programs in Canada leading to a CRPO designation.
How to Become a Therapist in British Columbia
To become a practicing therapist in B.C. you will need to:
- Complete a master’s degree in counselling or a related field.
- Undergo 100 hours of clinical supervision.
- Successfully complete the British Columbia Association of Clinical Counsellors (BCACC) examination.
How to Become a Therapist in Nova Scotia
To become a practicing therapist in Nova Scotia you will need to:
- Complete a master’s degree in counselling or a related field.
- Undergo supervised practice
- Successfully complete the Nova Scotia College of Counselling Therapists (NSCCT) examination.
How to Become a Therapist in New Brunswick
To become a practicing therapist in New Brunswick you will need to:
- Complete a master’s degree in counselling or a related field.
- Undergo supervised practice.
- Successfully complete the College of Licensed Counselling Therapists of New Brunswick (CCTNB) examination.
Quick Summary
Here is your six-step journey of succeeding as a therapist in Canada.
Step 1: Choose Your Specialization
Step 2: Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree
Step 3: Pursue Higher Education
Step 4: Gain Clinical Experience
Step 5: Obtain Licensure or Registration
Step 6: Continue Professional Development
Earn an MA in Counselling Psychology Without Putting Your Life On Pause
Become a Registered Counsellor or Psychotherapist with Yorkville University’s online Master of Arts in Counselling Psychology (MACP) program.
Program highlights:
- Accelerated: Earn your degree in as few as 2.5 years.
- Flexibility: Balance your education with life’s demands through our adaptable online format.
- Extensive Network: Join over 11,000 alumni and leverage our 2,400+ approved practicum sites to gain real-world experience.
- Fully Online: Complete your MACP entirely online, providing you with the flexibility to learn from anywhere.
Sound interesting? Speak with one of our admissions advisors for more information.
How to Become a Therapist in Canada FAQ
Q: What are the characteristics of effective mental health practitioners?
A: Effective mental health practitioners demonstrate empathy, active listening, cultural competence, and strong communication skills. They also possess the ability to create a safe and non-judgmental space for clients.
Q: How can I become a psychotherapist in Ontario?
A: To become a psychotherapist in Ontario, you need to complete a graduate program in psychotherapy or counseling, accrue supervised clinical experience, and obtain a registration with the College of Registered Psychotherapists of Ontario (CRPO).
Q: What are the education and training requirements to become a professional counsellor?
A: The education and training requirements to become a professional counsellor typically include completing a bachelor’s degree in psychology, counseling, or a related field, and then pursuing a master’s degree in counseling or clinical mental health.
Q: What are the salary expectations for mental health practitioners?
A: The salary expectations for mental health practitioners can vary based on factors such as location, experience, and specialization. On average, licensed therapists, counselors, and psychotherapists can earn competitive salaries, especially in private practice or specialized areas of mental health.
Q: How can I become a licensed therapist?
A: To become a licensed therapist, you typically need to complete a graduate program in counseling or clinical mental health, accrue supervised clinical experience, and obtain licensure through the regulatory board or agency in your state or country.
Q: What are the requirements for becoming a psychologist in Canada?
A: In Canada, becoming a psychologist typically requires completing a doctoral degree in psychology, obtaining supervised clinical experience, and obtaining registration or licensure through the regulatory body in the province where you plan to practice.
Q: What is the process to become a counselor or psychotherapist in private practice?
A: The process to become a counselor or psychotherapist in private practice involves completing the necessary education and training, obtaining licensure or registration, building clinical experience, and establishing a professional practice that adheres to ethical and legal standards.
Q: What are the steps to become a registered psychotherapist in Ontario?
A: The steps to become a registered psychotherapist in Ontario involve completing an accredited graduate program in psychotherapy, gaining supervised clinical experience, and obtaining registration with the College of Registered Psychotherapists of Ontario (CRPO).
Q: What is the typical process to become a licensed psychiatrist?
A: The typical process to become a licensed psychiatrist involves completing a medical degree, obtaining licensure as a physician, completing a psychiatric residency program, and obtaining board certification in psychiatry.
Q: What is the path to becoming a social worker in the mental health field?
A: The path to becoming a social worker in the mental health field involves completing a bachelor’s or master’s degree in social work, obtaining licensure or registration as a social worker, and gaining specialized experience or training in mental health settings.